Magnitude Resultant Force Acceleration
Determine the acceleration of a mass of 24 kg when a force of magnitude 6 N acts on it. What is the magnitude of the resultant acceleration of point on the tip of the blade at time 0200 Homework Equations none given the angular velocity at time 0200 is 043 the tangential speed at time 0200 is 103 ms The Attempt at a Solution I have tried doing sqrttangential acceleration2 radial acceleration2 my answer attempts are 279 277 195.

Force Acceleration Cie As Physics Revision Notes
A The total vector force is F m a 3.
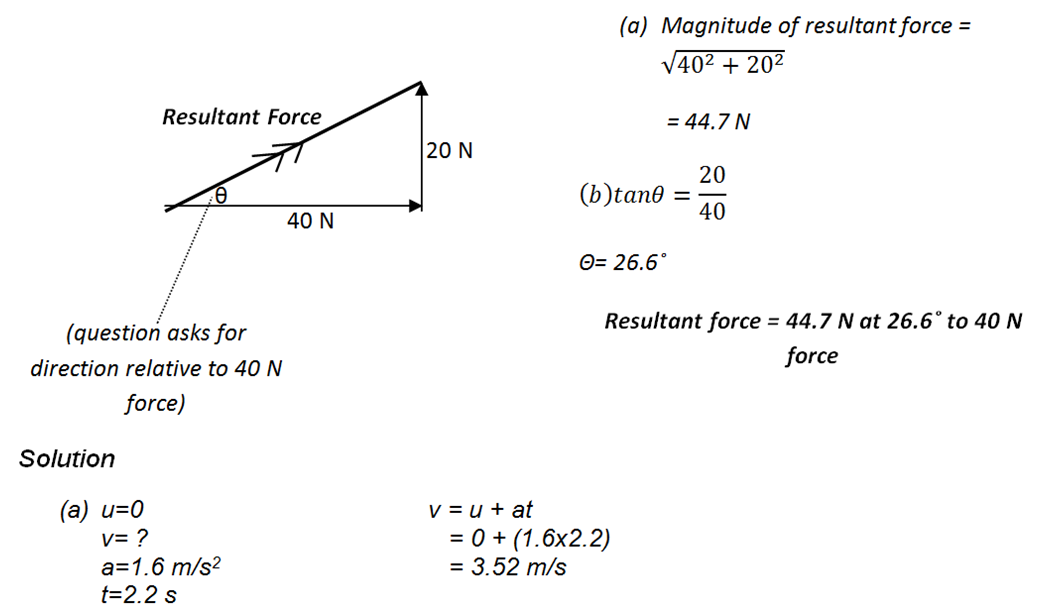
Magnitude resultant force acceleration. 0 0 k g 2. The resultant force could also be at an angle in which case addition of vectors is used to find the magnitude and direction of the resultant force. When an object is subject to several forces the resultant force is the force that alone produces the same acceleration as all those forces.
The givens are m 3. The resultant horizontal force 3500500 3000 N. This resultant force the centripetal force causes the centripetal acceleration.
0 N 2 1 6. Extending the link the angle the hypotenuse makes with the base is the direction of the force. 0 j N b Its magnitude is F F x 2 F y 2 6.
0 0 i 5. When a particle of mass m is acted upon by a force the acceleration of the particle must satisfy F r F ma r r Acceleration must be evaluated with respect to a Newtonian frame of reference ie one that is not accelerating or rotating. Newtons Second Law of Motion states that the acceleration of an object as produced by a net force is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force in the same direction as the net force and inversely proportional to the mass of the object.
The magnitude of a vector is the length of the vector. If force acting on particle. The magnitude of the net force in N.
Magnitude and angle of the resultant force KristaKingMath - YouTube. The magnitude of the vector a is denoted as a. Unsupported equation acceleration ms 2 a resultant force N mass kg F m Usually written.
Determine the magnitude and direction of theresultant force. Particle will have an acceleration proportional to the magnitude of resultant and in the direction of the resultant. If the net force acting on an object is zero then the object is not accelerating and is.
The magnitude of the resultant force of the two forces. 0 0 i 1 5. A Nissan LEAF has mass 1557kg.
A resultant force opposite to the direction of motion slows it down. Get full lessons more subjects at. For a two-dimensional vector aa1a2 the formula for its magnitude is aa21a22.
For more details on this have a look at the page on Scalars Vectors Acceleration. 0 0 N 2 1 5. Newtons Second Law formula.
The magnitude of the resultant acceleration of the object is 214 ms2. 0 0 k g and a 2. This is just a few minutes of a complete course.
0 0 j m s 2. Acceleration a is measured in metres per second squared ms The equation shows that the acceleration of an object is. See the introduction to vectors for more about the magnitude of a vector.
Calculate the magnitude of the resultant force that is causing the acceleration. Given the mass Newtons Second Law means you can find the acceleration of an object. Force diagram of forces on caravan ii Calculate the magnitude and direction of the resultant force on the caravan.
Unsupported equation resultant force N F mass kg acceleration ms 2 m a. What is the acceleration if the force were doubled and the mass was halved. A force of 200 N acting at 60 degrees to the horizontal accelerates a block of mass 50 kg along a horizontal plane.
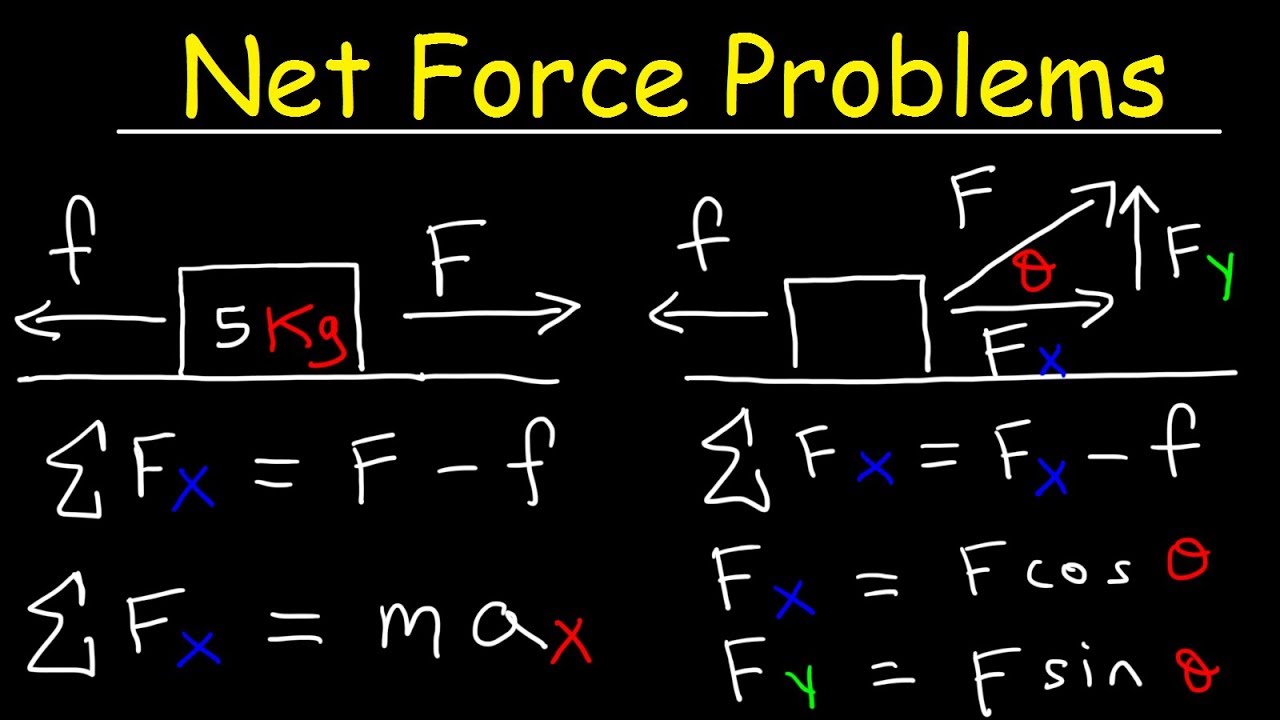
If it accelerates at 23ms2 what is the unbalanced force on it. To calculate the magnitude of force vectors you use the components along with Pythagoras theorem. Magnitude and Equation The magnitude of the net force acting on an object is equal to the mass of the object multiplied by the acceleration of the object as shown in the formula below.
Iii Calculate the acceleration the caravan experiences. The resultant force could also be at an angle in which case addition of vectors is used to find the magnitude and direction of the resultant force. Think of the x coordinate of the force as the base of a triangle the y component as the height of the triangle and the hypotenuse as the resultant force from both components.
We use Newtons second law to find the force as a vector and then the Pythagorean theorem to find its magnitude. A resultant force in the direction of motion speeds an object up. 0 0 j m s 2 6.
For example if 4 forces act on a block and cause it to accelerate 1 ms 2 south then the resultant force is the force that if applied alone to the block will also make it accelerate 1 ms 2 south. The force here as calculated in part ii is 3000 N to the right and the mass of the caravan is 1000 kg. For more details on this have a look at the page on Scalars Vectors Acceleration.
F m a Where. Magnitude and angle of the resultant force KristaKingMath Watch later. Proportional to the resultant force on the object inversely proportional.
0 0 i 5. However the magnitude or how much the change is will depend upon the objects mass. MathsGee Answers Explanations Join the MathsGee Answers Explanations community and get study support for success - MathsGee Answers Explanations provides answers to subject-specific educational questions for improved outcomes.
Similarly what is the magnitude of the resultant force of the two forces. Given the mass Newtons Second Law means you can find the acceleration of an object.
Calculating Net Force And Acceleration Dummies
Net Force Physics Problems With Frictional Force And Acceleration Youtube

Find The Magnitude Of The Resultant Force And The Angle It Makes With The Positive X Axis Study Com

Calculating Resultant Forces Vector Diagrams Graphs Work Done Calculations Equilibrium Parallelogram Of Forces Tension Vector Forces Gcse 9 1 Physics Igcse Revision Notes

Newton S Second Law Newton S Second Law States The Resultant Force On A Body Is Proportional To The Acceleration Of The Body In Its Simplest Form Ppt Download

Magnitude And Angle Of The Resultant Force Kristakingmath Youtube

Determine The Magnitude And Direction Of The Resultant Force Youtube

A Determine The Magnitude Of The Resultant Force F F2 F3 B Determine The Direction Phi Of The Resultant Force F F2 F3 Measured Counterclockwise From The Positive X Axis C Determine The Mag Study Com

Determine The Magnitude Of The Resultant Force And Its Direction Measured Counterclockwise From The X Axis For The Figure Below Study Com
What Is The Resultant Force And How To Find It With Examples Phyley

Newton S Laws S4 Physics Revision

A Level Maths R5 01 Forces Magnitude And Direction Of Acceleration Youtube

Four Forces 8n 6n 2n And 4n Act On A Point O In The Directions North East South And West Respectively Find The Magnitude Of Their Result And The Direction Of Their Resultant Force Study Com

A Determine The Magnitude Of The Resultant Force And Its Direction Measured Counterclockwise From The Positive X Axis B Express F 1 F 2 And F 3 As Cartesian Vectors Study Com
What Is The Resultant Force And How To Find It With Examples Phyley

Uniform Circular Motion Centripetal Force Youtube

Calculating Net Force In 2 D Youtube

Newton S Second Law Newton S Second Law States The Resultant Force On A Body Is Proportional To The Acceleration Of The Body In Its Simplest Form Ppt Download
What Is The Resultant Force And How To Find It With Examples Phyley
Posting Komentar untuk "Magnitude Resultant Force Acceleration"