Equation Of Resultant Vector
A resultant vector is defined as a single vector whose effect is the same as the combined effect of two or more vectors. In this Physics video in Hindi for class 11 we derived the formula for the magnitude and the direction of the resultant vector of two vectors having a certai.

Determine Resultant Of Two Vectors Using Pythagorean Theorem Solved Problems In Basic Physics
Methods for calculating a Resultant Vector.

Equation of resultant vector. Resultant of two vectors at an angle resultant vector angle formula resultant vector equation. Vector subtraction is similar to vector addition. The two vectors to be added should have the same nature.
Note that the equation is just the Pythagorean theorem relating the legs of a right triangle to the length of the hypotenuse. The resultant vector is the total of the four individual vectors or 200 pounds which should be equal and opposite to the weight of the master and the vehicle. We can write the equation for the resultant vecF_R as.
The quantities that have both magnitude and direction are called vectors. The head to tail method to calculate a resultant which involves lining up the head of the one vector. This equation confirms that when a resultant force acts on an object it will cause a change of momentum in the direction of the force and the size of the change depends on the size of.
Well using polar cordinates we can write the cartecian cordinate through x y z r c o s s i n r s i n s i n r c o s this is simple trigometry if you think about it. Above equation is the magnitude of the resultant vector. The resultant vector travels directly from the beginning of u to the end of v in a straight path as shown in Figure.
In order to find the. Resolve the resultants components to find the magnitude and direction of the resultant vector using the R to P procedure described in Subsection 233. Learn more about resultant vector example problems with solutions.
Which indicates that the resultant force R has the same direction as a and has magnitude equal to the product m a. The lengths of the perpendicular sides of the right triangle are 80 m North 60 km 20 km and 60 km East. There are a two different ways to calculate the resultant vector.
Multiple forces acting on an object - is the resultant force zero equilibrium or otherwise. The sum u v is the resultant vector because it results from addition or subtraction of two vectors. For 0 0 1 we have r 1 and 0.
Often however we know the forces that act on an object and we need. To say that vector R is the resultant displacement of displacement vectors A B and C is to say that a person who walked with displacements A then B and then C would be displaced by the same amount as a person who walked with displacement R. Force can be added to force and velocity can be added to velocity but the force cannot be added to the velocity.
Let be the angle between P and Q and R be the resultant vector. Create vector equations for each of the given forces add the vector equations together to get the vector equation of the resultant force find magnitude of the resultant force using the new vector equation and the distance formula Dsqrt left x_2-x_1right2left y_2-y_1right2 D. Note that this relationship between vector components and the resultant vector holds only for vector quantities which include both magnitude and direction.
Displacement vector R gives the same result as displacement vectors A B C. A x A y A. A resultant vector is a combination or in simpler words can be defined as the sum of two or more vectors which has its own magnitude and direction.
The resultant vector is the vector that results from adding two or more vectors together. Resultant vector Explanation and Examples. The magnitude and direction of the resultant vector can be determined once the horizontal and vertical components and have been determined.
A x and A y are defined to be the components of A along the x and y-axesThe three vectors A A x and A y form a right triangle. The magnitude of the resultant vector R can be determined using the Pythagorean theorem. After rearranging the order in which the three vectors are added the resultant vector is now the hypotenuse of a right triangle.
Then according to parallelogram law of vector addition diagonal OB represents the resultant of P and Q. In vector geometry the resultant vector is defined as. Lastly the students learn how to utilize the Universal Wave Equation.
For example if a box of 15 kg is subject to 5 forces which make it accelerate 20 ms 2 north-west then the resultant force is directed north-west and has the magnitude equal to 15 kg 20 ms 2 30 N. To determine the direction of the resultant vector let be the angle between the resultant vector R and P.

Resultant Vector Definition Formula Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Vector Application Find Magnitude And Angle Of The Resultant Force Youtube
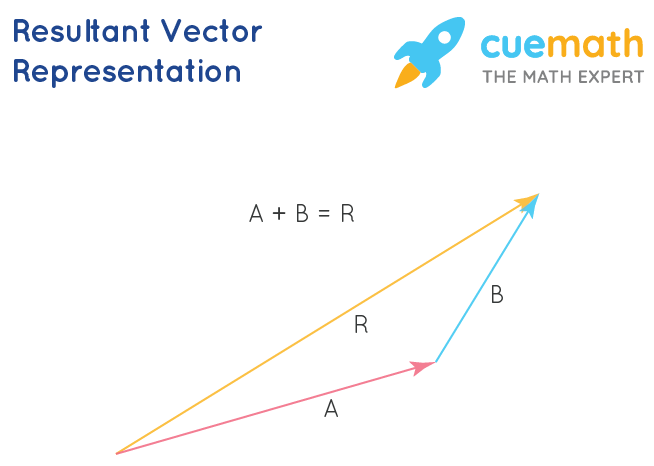
Resultant Vector Formula Learn To Find The Resultant Vector

Find The Magnitude And Direction Of The Resultant Of Two Vectors A And B In The Terms Of Their M Youtube
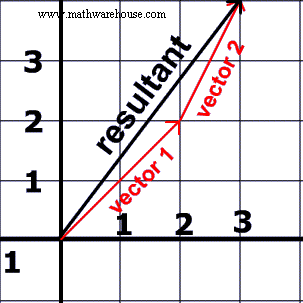
Resultant Vector How To Calculate A Resultant Using The Parallelogram Method And The Head To Tail Method A Resultant Is Simply

Formula Of Resultant Of Two Vectors Youtube
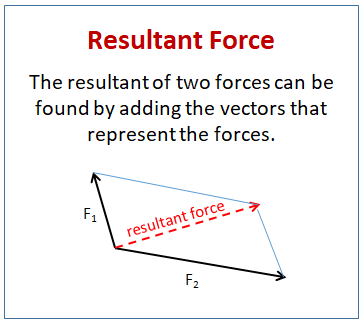
The Resultant Of Two Forces Solutions Examples Videos Worksheets Games Activities
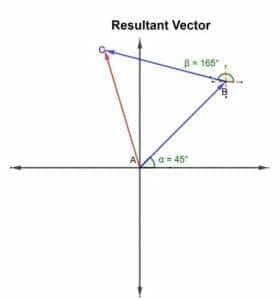
Calculating Resultant Vector Using Rectangular Components

Vector Application Find Magnitude And Angle Of The Resultant Force Youtube

Question Video Measuring The Magnitude Of A Resultant Vector Nagwa

Question Video Finding The Resultant Of Two Vectors Using The Parallelogram Method Nagwa

Resultant Vector Definition Formula Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
Resultant As Magnitude And Direction Ck 12 Foundation
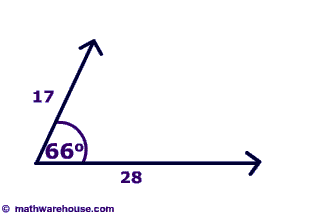
Resultant Vector How To Calculate A Resultant Using The Parallelogram Method And The Head To Tail Method A Resultant Is Simply

Lesson 1 Vector Addition Numerical
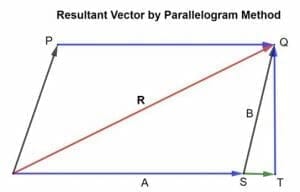
Calculating Resultant Vector Using Rectangular Components

Question Video Measuring The Magnitude Of A Resultant Vector Nagwa


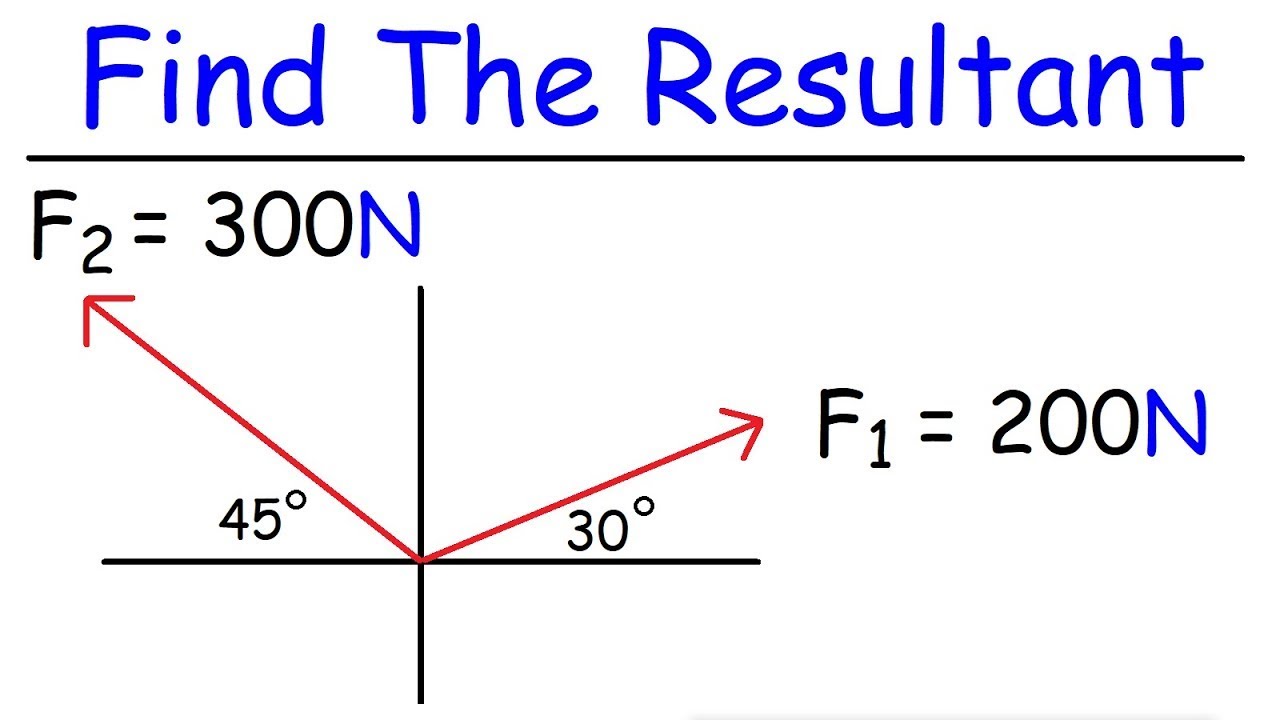
Posting Komentar untuk "Equation Of Resultant Vector"