How To Solve Resultant Velocity
Vm Sum SqrtVxi2VYj2 Where Vm is the resultant velocity magnitude. The head to tail method to calculate a resultant which involves lining up the head of the one vector with the tail of the other.

The Fnet M A Concept Builder Targets The Concept Of Net Force And Its Relationship To Mass And Acceleration Learn Physics Projects Body Diagram Newtons Laws
The resultant speed of the swimmer is 5 32 2 32 2 358 kmhr.

How to solve resultant velocity. Lets solve an example find the resultant of two vectors where the first vector has a magnitude of 30 and the second vector has a magnitude of 40 with 50 has the inclination between the two vectors. If the initial velocity was 0 ms then the. Use the equation ay a sin theta to find the y coordinate of the acceleration.
This is the same procedure that was used above for the headwind and the tailwind situations. It should be noted that the direction of the wind istakwn into consideration. Now inserting these values into the formula we compute for the resultant of the two vectors.
For example if an object falls for 3 seconds multiply 3 by 98 meters per second squared which is the acceleration from gravity. The average velocity calculator solves for the average velocity using the same method as finding the average of any two numbers. The Attempt at a Solution I know that the resultant velocity is the hypotenuse which means that 4232v2 where v5 mih.
15 x sin 63 degrees or 134. The resultant velocity of the plane ilwill be gotten by adding the value of the velocities of the plane with the tallwind. Question on Resultant Velocity.
Since the two vectors to be added - the southward plane velocity and the westward wind velocity - are at right angles to each other the Pythagorean. Vx is the magnitude of the x-component of the resultant velocity. Resultant Velocity Formula.
To calculate velocity using acceleration start by multiplying the acceleration by the change in time. Therefore the resultant velocity of the plane will be. Thus the total resultant velocity of the swimmer is the sum of these velocities v1 v2 which is 5 32 2 32 2 288 212.
Hence each hour the swimmer is traveling about 29 km east and 21 km north. For example if the acceleration is 10 ms2 and the change in time is 5 seconds then there is a 50 ms increase in velocity. 20kmhr 150kmhr 170kmhr to the South.
There are a two different ways to calculate the resultant vector. Given v and u calculate v. Calculate v v u 2.
The direction is calculated by finding the angle theta between the resultant velocity and the horizontal axis theta arctan yx where x is the magnitude of the x component and y is the magnitude of the y component. Methods for calculating a Resultant Vector. The following formula is used to calculate a resultant velocity.
Resultant Velocity - YouTube. Average velocity v of an object is equal to its final velocity v plus initial velocity u divided by two. Only now the resultant is not as easily computed.
The resultant vector is the vector that results from adding two or more vectors together. Convert the original velocity into vector component notation. If the current is flowing east at a rate of 3 miles per hour find the resultant velocity of the boat.
Va Tan-1 VxVy Where Va is the angle of the resultant velocity. How Do I Calculate Resultant Velocity. Then add the initial velocity to the increase in velocity.
Vectors Introduction and Examples. R 30 40 2. If the initial velocity was 2 ms then the final velocity is 52 ms.
The whole answer in the textbook. Vy is the magnitude of the y-component of the resultant velocity. To determine the resultant velocity the plane velocity relative to the air must be added to the wind velocity.
And thats only part of the answer. Question on Resultant Velocity. Videos you watch may be added to the TVs watch history and influence TV recommendations.
The resultant is the result of combining the individual vectors together. The resultant velocity in this case is 294 meters per second. From the example above we can see that P is 30 Q is 40 and is 50.
Vyj are all of the y-component of velocities. A boat heads north across a river at a rate of 4 miles per hour. Resultant velocity for two velocity components resultant_velocity sqrtVelocity component at u2 Velocity component at v2 Go Angular velocity considering the depth of parabola angular_velocity sqrtDepth of parabola2981 Radius 12 Go Depth of parabola formed at the free surface of water depth_of_parabola Angular Velocity2 Radius 12 2981 Go Rate of flow or discharge.
How do you find velocity with two directions. How do you calculate resultant. A is the resultant angle For example if theres a force of 10 Newtons acting in the positive x-direction and a force of 5 newtons acting in the -x direction the results for is 10 -5 5 newtons in the positive x-direction.
The parallelogram method to calculate resultant vector. Vxi are all of the x-component of velocities. In summary the resultant is the vector sum of all the individual vectors.
If playback doesnt begin shortly try restarting your device. Convert the acceleration into components. Multiply the acceleration by the time the object is being accelerated.

Relative Velocity Example 1 River Crossing Still Water River Example

Graph That Motion Motion Graphs Physics Classroom Physics

Finding Resultant Force From 2 Forces At 0 To 90 Degree Physics And Mathematics 90 Degrees Physics

Head To Tail Addition Is A Concept Builder That Provides Learners With An Exercise In Recognizing The Proper Vector Body Diagram Progress Report Understanding

Initial Velocity Components Physics And Mathematics Physics Classroom Physics Topics

Vector Cross Product Dgm Calculus Zero Point Energy Chapter

Vector Addition Concept Builder An Interactive Tool That Challenges The Learner To Use An Understanding Of Head Body Diagram Interactive Tools Progress Report

Math Principles Inclined Plane Problems 3 Inclined Plane Math Plane

Math Principles Rate Distance And Time Problems 9 Basic Algebra Still Water Math

Projectile Motion Of A Tennis Ball Teaching Resources Projectile Motion Engineering Science Tennis Ball

Constant Acceleration Equations Acceleration Equation Equations Acceleration

Vector Addition Physics Classroom Math Foldables Mathematical Equations

Vector Cross Product Dgm Calculus Zero Point Energy Chapter

Resultant Force Time Graph Link To Speed Time Graph Learn Physics Physics Classroom Physics Notes

Non Horizontally Launched Projectiles Problem Solving Physics Classroom Word Problems Physics

Graphs Of Motion Part 2 Graphing Physics Math

Component Addition Concept Builder Challenges Learners To Apply Vector Principles And Mathematics In Order To Determine The M Concept How To Apply Mathematics
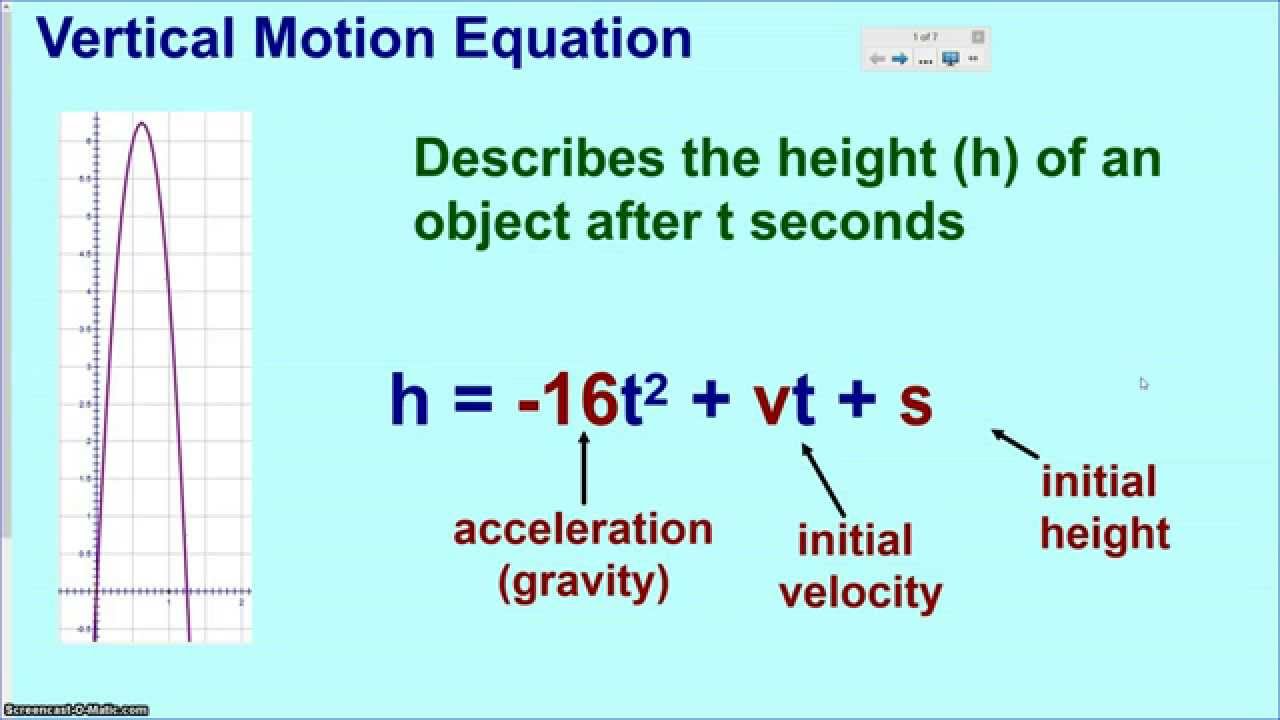
Vertical Projectile Motion Graphing Quadratics Word Problem Worksheets Math Problem Solving Strategies

Posting Komentar untuk "How To Solve Resultant Velocity"