The Resultant Amplitude When Two Waves Of Same Frequency
Resultant Frequency of two unlike soundwaves. Two sinusoidal waves of the same frequency are to be sent in the same direction along a taut string.

Interference Definition Examples Facts Britannica
If two identical waves are traveling in the same direction with the same frequency wavelength and amplitude.

The resultant amplitude when two waves of same frequency. Waves on the glass of milk are one example of standing waves. The resultant looks like a wave standing in place and thus is called a standing wave. If two sinusoidal waves having the same frequency and wavelength and the same amplitude are travelling in opposite directions in the same medium then using superposition the net displacement of the medium is the sum of the two waves.
What is the resultant amplitude if the phase angle is 1 2 2. When 0 crest to crest and trough to trough then cos 2 1. 0 m m the other 8.
Resultant wave is A 1 A 2 2A. If you superimpose two waves of different frequencies you will end up with a beat frequency equal to the difference of their frequencies. The resultant amplitude when two waves of two waves of same frequency but with amplitudes a_1 and a_2 superimpose at phase difference of pi2 wil.
The frequency of the resultant wave of 2 waves that are the same frequency is the same as the original because the pattern of constructive and destructive interference would repeat each wavelength. Start studying Physics-Chapter 7. When 0 crest to crest and trough to trough then cos 2 1.
Related Threads on What is the resultant frequency if two similar waves superpose. If the two waves have the same amplitude and wavelength then they alternate between constructive and destructive interference. When 2 waves of the same phase pass a point at the same time the resultant wave is larger than the original with twice the amplitude Click again to see term 124.
This is constructive interference. The green wave is the result of the superposition of the two waves. The pattern produced in standing waves can be seen only if there exists a repeated constructive interference of two waves such that they have same amplitude and frequency but they must be travelling opposite to each other in the same medium.
They interfere at a point where their phase difference is 380. When the two waves have a phase difference of zero the waves are in phase and the resultant wave has the same wave number and angular frequency and an amplitude equal to twice the individual amplitudes part a. Amplitude equals 2A cos 2 with a phase angle of 2.
The amplitude A of the resultant wave is given by squaring and adding Eqs. Destructive interference occurs when two interfering waves have displacements in opposite directions. The resultant looks like a wave standing in place and thus is called a standing wave.
The resultant sinusoidal wave has the same frequency and wavelength as the original waves but the amplitude has changed. When the two interfering waves are out of phase ivarphi ipi. The resultant amplitude of two interfering waves is equal to the sum of those two waves displacements at the same location as the resultant waves amplitude.
If the two waves have the same amplitude and wavelength then they alternate between constructive and destructive interference. Resultant wave is A1 A2 2A. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools.
It has the same frequency as that of the interfering waves. A wave of the same frequency and twice the amplitude of each incoming wave. The resultant amplitude of the wave we get through the combination of the two interfering waves is equal to the addition of the displacements of those two waves at the same location as the.
One wave has an amplitude of 5. What is the resultant amplitude. Consider two sound waves travelling with the same speed and amplitude but having similar but slightly different wavelengths _1 and _2 and angular frequencies _1 and _2.
The amplitude of the. BUT differ in phase the waves add together. Two waves of the same frequency have amplitudes 0901 and 155.
The resultant wave at Point A is a. The resultant wave Two waves of equal amplitude and the same frequency arrive in phase at a certain point A. Thus the amplitude of the resultant wave is maximum when the two interfering waves are in phase.
If two waves superimpose with each other in the same phase the amplitude of the resultant is equal to the sum of the amplitudes of individual waves resulting in the maximum intensity of light this is known as constructive interference. The waves move through each other with their disturbances adding as they go by.

Wave Interference Constructive Interference Destructive Interference
The Resultant Amplitude Of Two Superposed Waves Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Superposition And Interference Physics
Two Waves Of The Same Frequency And Same Amplitude Are Reaching A Point Simultaneously What Should Be The Phase Difference Between The Waves So That The Amplitude Of The Resultant Wave Is 2a

Two Waves That Add To Give A Resultant With The Same Amplitude Youtube
Adding Waves Of The Same Frequency Together
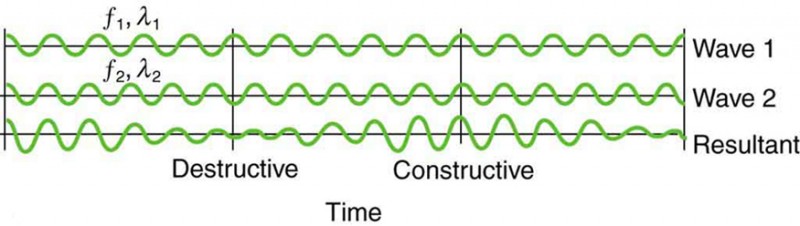
Superposition And Interference Physics
What Happens If Two Waves Of The Same Frequency And Equal Amplitude Superimpose Quora

Question Video Identifying The Resultant Of Two Interfering Waves Nagwa

Two Waves Having Equation S X 1 Asin Omegat Phi 1 X 2 Asin Omegat Phi 2 If In The Resultant Wave The Frequency And Amplitude Remain Equal To Those Of Superimposing Waves Then Phase Difference Between Them Is

If The Two Waves Of The Same Frequency And Same Amplitude On Superposition Youtube

Interactions With Sound Waves Boundless Physics

Is It Possible That Two Wave Have Different Amplitude And Same Frequency Quora

Question Video Identifying The Resultant Wave Of Two Waves Interfering Nagwa
Resultant Amplitude And Intensity Myrank

Two Waves Of Equal Amplitude And Frequency Interfere Each Other The Ratio Of Intensity When Th Youtube

The Resultant Amplitude When Two Waves Of Two Waves Of Same Frequency But With Youtube

Posting Komentar untuk "The Resultant Amplitude When Two Waves Of Same Frequency"